Describe the composition and structure of the atmosphere pdf
The troposphere is the lowest level of Earth’s atmosphere and extends from the surface to about 14.5 kilometers. The stratosphere is the second of Earth’s layers of the atmosphere and extends for
* The atmosphere is composed of gases, water vapour and dust particles * The proportion of gases changes in the higher layers of the atmosphere in such a way that oxygen will be almost in negligible quantity at the height of 120 km * Similarly, carbon dioxide and water vapour are found only up to 9o km from the surface of the earth.
Composition of the Atmosphere 17.1 Atmosphere Characteristics Weather is constantly changing, and it refers to the state of the atmosphere at any given time and place. Climate, however, is based on observations of weather that have been collected over many years. Climate helps describe a place or region. Composition of the Atmosphere 17.1 Atmosphere Characteristics Major Components • Air …
Introduction This section examines the atmosphere as a system, and several atmospheric phenomena that have become critical in the understanding and guardianship of our environment. The current state of the atmosphere is the result of a multitude of
Students will learn about the composition and structure of the atmosphere by creating a flip book of the layers of the atmosphere using the jigsaw strategy. In the summative assessment, students will write an article describing how the layers of the atmosphere sustain life on our planet.
Composition of the atmosphere Except for water vapor, whose atmospheric abundance varies from practically zero up to 4%, the fractions of the major atmospheric components N 2 , O 2 , and Ar are remarkably uniform below about 100 km.
(ii) Draw a suitable diagram for the structure of the atmosphere and label it and describe it. Answer The atmosphere consists of different layers with varying density and temperature.
In this chapter we describe the chemical composition of the atmosphere and key physical properties of air. We discuss the equation of state of air (the connection between pressure, density and temperature) and key properties of moist air. In particular, we will learn that warm air usually holds much more moisture than cold air, a fact that has enormous implications for the climate of the
Above 50 miles, the chemical composition of the atmosphere changes with altitude. This layer is known as the upper atmosphere or heterosphere. This upper layer is also known as the thermosphere and it extends outward several thousand miles with no real boundary between the upper atmosphere and space. Fig. 2: Layers of the atmosphere (NASA) Though the atmosphere extends outward several …
Introduction. The earth’s atmosphere is the layer of gases and aerosols surrounding the planet and held by the earth’s gravitational force. The composition and structure of the atmosphere define its role, both as a producer of weather and a protector of life.
1 ATMO 1300 Chapter 1- Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere Understanding Weather and Climate Aguado and Burt 1/2008 VERSION ATMO 1300 Definitions
Structure of the atmosphere. We commonly think of gas molecules as moving about in a completely random manner, but the Earth’s gravitational field causes downward motions to be very slightly favored so that the molecules in any thin layer of the air collide more frequently with those in the layer below.
Structure and composition of the Earth The overall composition of the Earth is very similar to that of meteorites, and because of this, it is thought that the Earth originally formed from Planetesimals composed largely of metallic iron and silicates.
Composition of the Atmosphere unacademy.com

ATMOSPHERE COMPOSITION AND STRUCTURE nios.ac.in
Atmosphere: Structure and composition, and distribution of heat (Chapter 16) The gaseous layer of Earth is its atmosphere. In studying Earth’s atmosphere, we can study the weather and climate.
ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE. The vertical distribution of temperature, pressure, density, and composition of the atmosphere constitutes atmospheric structure. These quantities also vary with season and location in latitude and longitude, as well as from night to day; however under the topic of atmospheric structure, the focus is on the average variations with height above sea level. Although it …
Atmosphere Our planet earth is enveloped by a deep blanket of gases extending several thousands of kilometres above its surface. This gaseous cover of the earth is known as the atmosphere. Like land (lithosphere) and water (hydrosphere), the atmosphere is an integral part of the earth. Compared to the earth’s radius, the atmosphere appears to
The structure of the atmosphere dictates the way the atmosphere behaves and controls how weather develops near the surface of the earth. I should already be familiar with: Humidity, Temperature, Pressure, Density. Figure A: The Layers of the Atmosphere (Image from the Comet Program) The atmosphere consists of 4 layers: the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and thermosphere. …
Structure of the Atmosphere Scientists divide the atmosphere into four layers that are based on temperature changes. The layer closest to the earth is called the troposphere .
atmosphere is equal to the total weight of the gas above that level. The hydrostatic equation: dP(z) / dz = – ρ (z) g [6.4] where ρ (z) is the mass density of air at height z, and g is the acceleration of gravity.
Start studying Chapter 1: Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Atmosphere 2.1. Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere 2.2. Physics of the Atmosphere 2.3. Chemistry of the Atmosphere 2.4. The Atmosphere as a Colloidal Medium 2.5. Nature of Atmospheric Circulation 2.6. Modeling of Atmospheric Circulation 3. Hydrosphere 3.1. Atmospheric Waters 3.2. Hydrological Cycle on the Earth 3.3. Surface Water 3.4. Ice in the Hydrosphere 3.5. …
atmospheric composition, temperature & function The earth’s atmosphere is a reservoir of gases. Air is a mixture of gases that is naturally odorless, colorless, tasteless and formless.
The teacher understands the structure and function of earth systems. Earth Science describes the structure and composition of earth and how it has changed over time. It is crucial to many aspects of human life and the production of resources.

The structure and composition of the atmosphere Next: 1.4. Vertical structure of the atmosphere . 1.4.1. Vertical change of composition. According to the homogeneity of atmospheric composition, two layers can be defined in the atmosphere. The lower layer, up to an altitude of about 80 km above sea level is the homosphere, where due to the continuous turbulent mixing the composition of the
learning goals •know the major atmospheric gases •describe the major greenhouse gas trends and explain the relative “strength” of some GHGs
Vertical Structure of the Atmosphere Part 1 Principle: The changes in the atmosphere with height are results of specific physical conditions which exist on the earth and in its atmosphere.
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere Chapter 1 Lecture Redina L. Herman Western Illinois University Understanding
Monitoring and Management > Human activity has caused changes in the composition and the structure of the atmosphere. Chemists monitor these changes so that further damage can be limited
6/05/2012 · Covers the HSC chemistry syllabus dot point: “describe the composition and layered structure of the atmosphere”
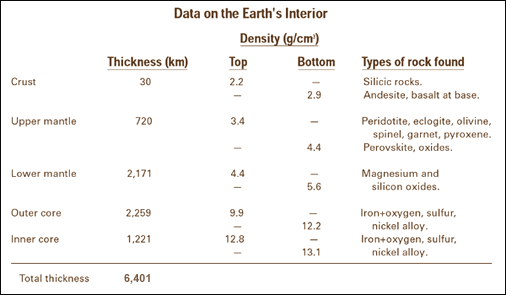
The solid component of earth is called Lithosphere. It consists of different layers viz. crust, mantle, outer core and inner core. The crust is the outermost solid layer of the earth. It is composed of different types of rocks which, as a whole, has the density and composition of granite. Hence the
Concept 2: Describe the physical and chemical features of the atmosphere including variations in composition, pressure, and thermal structure. Concept 3: Explain the causes of the seasons. Concept 4: Compare and contrast the definitions and properties concerning energy, light, heat, and temperature.
Air is a gaseous substance that is composed primarily of nitrogen, oxygen and argon. The air in the atmosphere that surrounds the Earth is approximately 78 percent nitrogen, 21 percent oxygen and 1 percent argon, with the remainder made up of various other gases including neon, helium and hydrogen.
thermal structure, the planet’s surface and interior composition, the high surface temperature, the stability of CO2, the ionosphere – its chemistry and thermal structure, the existence of superrotation,
Ist US-Brazil Fulbright Course on Biofuels, Sao Singh – Corn Structure and Composition Paulo, Brazil University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Cereal Grains Structure & Composition Vijay Singh Associate Professor Department of Agricultural & Biological Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL 1st Brazil-U.S. Biofuels Short Course São Paulo, Brazil July 27 – August
Describe the composition and layered structure of the atmosphere Atmosphere : The gaseous mixture surrounding the surface of the Earth. The dry atmosphere is composed of the following gases:
Chapter 1 Characteristics of the atmosphere MIT PAOC
Circle of Illumination- line separating the dark half of Earth from the lighted half. – Solstice is the beginning of winter and summer. – the sun is vertical at the latitude – Equinox is the beginning of fall and spring. – the sun is vertical at the latitude – it refers the equal
The Atmosphere Composition and Structure The Atmosphere 1 / 16. Outline of Topics 1 Intro to Air Pollution 2 Atmospheric Composition Concentration of Gases Particulate Matter 3 Structure of the Atmosphere Thermal Strati cation Mixing Times Spatial Variability of Composition 4 Light Nature of Light Sunlight The Atmosphere 2 / 16. Introduction to Air Pollution What are the major problems due …
An atmosphere is defined as the gaseousAn atmosphere is defined as the gaseous envelope that surrounds a celestial body.envelope that surrounds a celestial body. Therefore, the Earth, like other planets inTherefore, the Earth, like other planets in the solar system, has an atmosphere, whichthe solar system, has an atmosphere, which is retained by gravitational attraction andis retained by
10 Atmospheric Structure and Composition 237 The most signifi cant spatial variation in a planetary atmosphere is the vertical stratifi cation due to gravity and
1/06/2011 · The structure of our atmosphere!! Category Science & Technology; Show more Show less. Loading… Advertisement Autoplay When autoplay is enabled, a …
An atmosphere is a layer or a set of layers of gases surrounding a planet or other material body, that is held in place by the gravity of that body. An atmosphere is more likely to be retained if the gravity it is subject to is high and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. The atmosphere …
Composition: iron and nickel The Earth’s inner core is a huge metal ball, 2,500km wide. Made mainly of iron, the temperature of the ball is 5,000°C to 6,000°C – that’s up to 6,000 times hotter than our atmosphere and scorching enough to make metal melt!
The Atmosphere: Composition, Structure, and Temperature Earth Science, 13e Chapter 16 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Weather and climate Weather • Weather is over a short period of time • Conditions are constantly changing • State of atmosphere at any given point of time and place Climate • Climate is over a long period of time • Weather is collected over many
The Nature and Structure of the Atmosphere 1 – 3 occur in the atmosphere. Weather, on the other hand, is defined as the day to day state of the atmosphere at a …
atmosphere planet earth wikipediaplanet earth: facts about its orbit, atmosphere & sizethe composition of planetary atmospheres facts about earth – our solar system – astronomy for kidshow to describe the atmosphere of planet earth – quora – debbie meyer green bags instructions 16/05/2015 · First Video of the NCERT class 11 chapter Climate , Revise in 6 Minutes ,Subscribe for more such Videos -NCERT-Climate -Chapter 1- Video1.
NCERT Solutions Composition and Structure of Atmosphere
Atmospheric Structure and Composition
Atmosphere Planet Earth elab.businessinnovationfactory.com
Describe atmosphere detail its composition and structure
Structure and composition of the Earth Australian Museum
5. COMPOSITION AND STRUCTURE OF THE ATMOSPHERE
Atmosphere Role Structure & Composition PMF IAS
1.4. Vertical structure of the atmosphere ELTE TTK ONLINE
– Our Amazing Atmosphere CPALMS
Lithosphere It’s Physical Characteristics Compositions
Monitoring and Management The Atmosphere – EasyChem
Atmospheric Structure
Vertical Structure of the Atmosphere Part 1 Principle: The changes in the atmosphere with height are results of specific physical conditions which exist on the earth and in its atmosphere.
The Atmosphere Composition Structure and Temperature
5. COMPOSITION AND STRUCTURE OF THE ATMOSPHERE
Our Amazing Atmosphere CPALMS
Above 50 miles, the chemical composition of the atmosphere changes with altitude. This layer is known as the upper atmosphere or heterosphere. This upper layer is also known as the thermosphere and it extends outward several thousand miles with no real boundary between the upper atmosphere and space. Fig. 2: Layers of the atmosphere (NASA) Though the atmosphere extends outward several …
1. Cereal Grains Structure & Composition
Atmospheric Composition and Structure Geography – Oxford
Atmospheric Structure and Composition
The solid component of earth is called Lithosphere. It consists of different layers viz. crust, mantle, outer core and inner core. The crust is the outermost solid layer of the earth. It is composed of different types of rocks which, as a whole, has the density and composition of granite. Hence the
Atmosphere Planet Earth elab.businessinnovationfactory.com
Composition and structure of the atmosphere. Basic
V. Composition and structure of the atmosphere
learning goals •know the major atmospheric gases •describe the major greenhouse gas trends and explain the relative “strength” of some GHGs
Monitoring and Management The Atmosphere – EasyChem
1.4. Vertical structure of the atmosphere ELTE TTK ONLINE
5. COMPOSITION AND STRUCTURE OF THE ATMOSPHERE
Composition of the atmosphere Except for water vapor, whose atmospheric abundance varies from practically zero up to 4%, the fractions of the major atmospheric components N 2 , O 2 , and Ar are remarkably uniform below about 100 km.
ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION TEMPERATURE AND FUNCTION
In this chapter we describe the chemical composition of the atmosphere and key physical properties of air. We discuss the equation of state of air (the connection between pressure, density and temperature) and key properties of moist air. In particular, we will learn that warm air usually holds much more moisture than cold air, a fact that has enormous implications for the climate of the
Chapter 1 Characteristics of the atmosphere MIT PAOC
Competency 051 The Structure and Function of Earth
atmosphere is equal to the total weight of the gas above that level. The hydrostatic equation: dP(z) / dz = – ρ (z) g [6.4] where ρ (z) is the mass density of air at height z, and g is the acceleration of gravity.
COMPOSITION AND STRUCTURE OF ATMOSPHERE YouTube
Composition And Structure Of The Atmosphere EOLSS